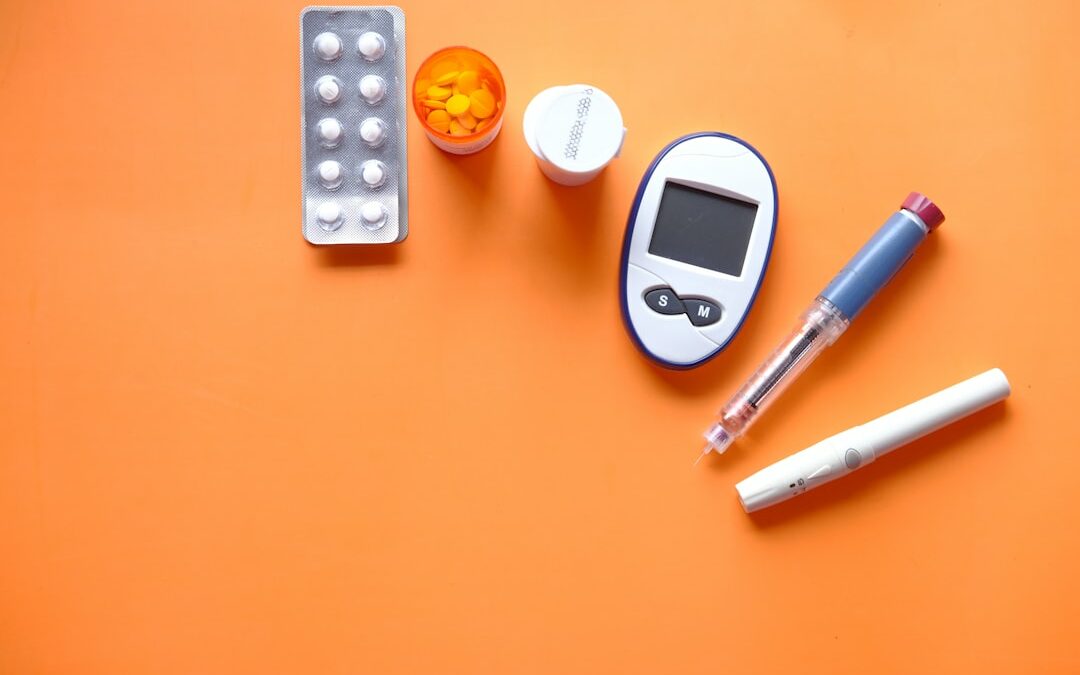
Blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. It involves measuring the amount of glucose (sugar) present in your bloodstream at various times throughout the day. Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes understand how their bodies respond to food, exercise, and medication, enabling them to make informed decisions about their treatment plan. By keeping track of blood sugar levels, individuals can prevent complications associated with high or low blood sugar levels, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Monitoring blood sugar also allows for timely adjustments in diet, physical activity, and insulin dosage, ensuring better control over diabetes and overall well-being.
What is Blood Sugar Monitoring?
Blood sugar monitoring, also known as self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), is a crucial practice for individuals with diabetes, as it allows them to track their blood sugar levels and make informed decisions about their diabetes management. This process involves measuring the concentration of glucose in the blood at various times throughout the day. By monitoring blood sugar, individuals can identify patterns, detect highs and lows, and adjust their treatment plan accordingly, including diet, physical activity, and medication dosages. Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for preventing or delaying the progression of diabetes-related complications, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues. With the help of modern technology and advancements in blood sugar monitoring devices, individuals can now conveniently and accurately monitor their blood sugar levels at home, empowering them to take control of their health and maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar at Home
Monitoring blood sugar levels at home is an essential part of managing diabetes effectively. It provides valuable insights into how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication, allowing you to make informed decisions about your treatment plan. There are two primary methods for home blood sugar monitoring: using a glucose meter and test strips or a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system.
Using a Glucose Meter and Test Strips
One of the most common and convenient methods for blood sugar monitoring is using a glucose meter and test strips. This portable device allows you to check your blood sugar levels at any time and anywhere. To use a glucose meter, you’ll need to prick your fingertip with a lancet and apply a small drop of blood onto a test strip, which is then inserted into the meter. The meter will analyze the blood sample and display your current blood glucose level within seconds. Glucose meters are easy to use and provide accurate results, making them an essential tool for those with diabetes or prediabetes. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for proper use and maintenance of your glucose meter and test strips. By regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels with a glucose meter, you can better manage your condition, make informed decisions about your diet and medication, and potentially prevent complications.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is an advanced method of blood sugar monitoring that provides real-time glucose readings 24 hours a day. Unlike traditional finger prick tests, CGM systems use a small sensor inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm. This sensor continuously measures the glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which closely reflects the blood sugar levels. The sensor is connected to a transmitter that sends the glucose data wirelessly to a receiver or a compatible smart device. CGMs can track glucose levels every few minutes, providing a comprehensive picture of glucose trends throughout the day and night. Many CGM devices also have customizable alerts to notify the user when glucose levels are outside the target range, allowing for timely intervention. This technology offers significant advantages, including improved diabetes management, reduced risk of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, and better overall blood sugar control.
Tracking Blood Sugar Levels
Tracking blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of blood sugar monitoring for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By keeping a record of your blood glucose readings, you can gain valuable insights into how your body responds to various factors like food, exercise, medication, and stress. This information can help you make informed decisions about managing your diabetes and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Tracking your blood sugar levels typically involves recording the date, time, and numerical value of each reading in a logbook, smartphone app, or digital device. Many glucose meters and continuous glucose monitoring systems automatically store this data, allowing you to easily review patterns and trends over time. Regular monitoring and tracking can help you identify when your blood sugar levels are outside the target range, enabling you to take appropriate action and make necessary adjustments to your lifestyle, diet, or treatment plan. Collaborating with your healthcare team and sharing your tracked data can lead to more personalized and effective diabetes management strategies.
How Often to Check Blood Sugar
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on several factors, including whether you have diabetes, the type of diabetes you have, and the treatment plan you’re following. For people without diabetes, occasional checks can provide insights into overall health, but regular monitoring is generally not necessary. However, for those with diabetes, regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing complications.
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, frequent blood sugar monitoring is essential. They should check their levels several times a day, typically before meals, before bedtime, and before engaging in physical activity. This helps determine the correct insulin dose and adjust it as needed based on food intake, exercise, and other factors. The recommended frequency may vary based on individual circumstances and healthcare provider recommendations.
For those with type 2 diabetes, the frequency of blood sugar monitoring can vary depending on the treatment plan and the individual’s ability to manage their condition. People with type 2 diabetes who are not taking insulin may need to check their levels less frequently, such as once or twice a day, or even a few times a week. However, those taking insulin or experiencing fluctuations in blood sugar levels may need to check more often, similar to individuals with type 1 diabetes. Regular monitoring helps identify patterns, adjust medication or lifestyle factors, and prevent potential complications.
Best Times to Check Blood Sugar
Checking blood sugar levels at specific times throughout the day is crucial for effective blood sugar monitoring. The best times to check include first thing in the morning before eating (fasting blood sugar), before meals, two hours after meals, before bedtime, and occasionally during the night. Fasting blood sugar levels provide a baseline measurement and help evaluate overnight glucose control. Pre-meal checks help determine the need for insulin or medication adjustments. Two-hour post-meal checks assess how your body responds to the food you’ve eaten. Bedtime checks help ensure safe overnight levels. For those with frequent low blood sugar episodes, night-time checks may be necessary. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the optimal testing schedule tailored to your individual needs and health conditions.